Overview of the Cooling Systems for Ball Screws
In practice, our ball screws impress with low friction and very low power loss. This allows us to achieve an extremely high degree of efficiency. The workpiece temperatures can increase nevertheless if they are used with high acceleration values or speeds. A.MANNESMANN offers a variety of cooling options for these high-load applications.
Targeted Temperature Control - for Consistent Operating Conditions
The cooling systems reduce the transfer of heat to the adjacent machine environment, thereby increasing the positioning accuracy of the ball screw linearly throughout the entire operating time. Furthermore, cooling reduces undesired preload and contributes to a constant lubricant viscosity during operation. All of this reduces wear and increases the service life.
Benefits of a Cooling System
Using a cooling system makes it possible to convincingly keep the operating temperature of the ball screw constant: The amount of coolant and inlet temperature can be controlled so that the temperature control is kept in tight tolerances.
In this way, the warm-up phase of machine tools is reduced significantly so that the production capability is already achieved after a very short time.
Thermal Requirements and Production
Speak to us about your thermal problems and requirements. We are happy to advise you with no obligation.
Of course we will be happy to produce custom cooling solutions for requirements that go beyond standard cooling systems.
General Advantages at a Glance

Economical advantages
- High travel speeds
- High acceleration values
- Less wear
- Longer service life
- Reduction of the warm-up phase, faster production capability
- 3 cooling versions possible (spindle, nut and combination)

Technical advantages
- Perfect positioning capability and repeatability
- High load capacity
- Exact travel movements
- High rigidity
- Ball screw spindles with ground precision (accuracy IT 1, IT 3, IT 5)
- Constant torque
- Extremely low power losses
- Uniformly low operating temperatures
- Can be used in all installation positions
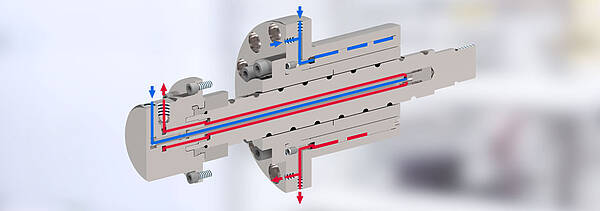
Three cooling systems
Depending on the task, cooling is available for the spindle unit, the nut or both workpiece elements.
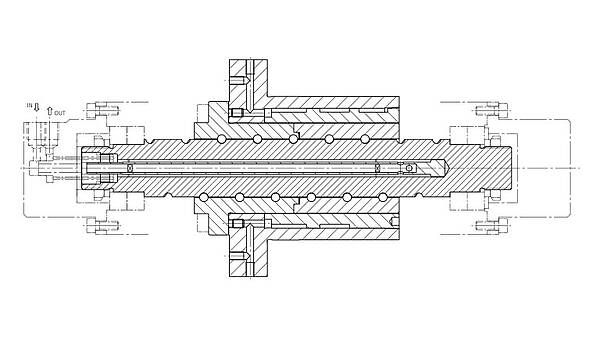
Cooling of the Ball Screw Spindle
A central bore through the entire spindle length is used to dissipate heat. Coolant flows through it and cools the spindle temperature down to the desired specific value.
Alternative versions of the cooling hole are also possible for special designs.

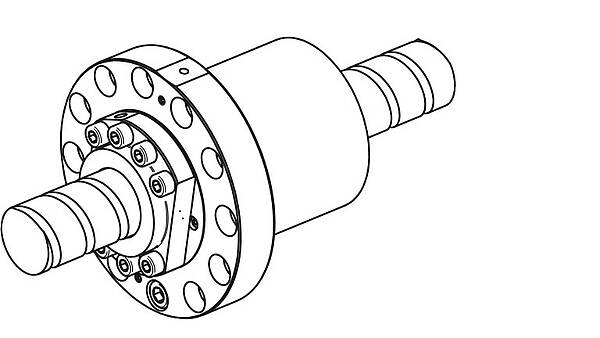
Cooling of the Ball Screw Nut
The ball screw nut is cooled via a cooling jacket, which is placed around the nut housing. It can also be designed as an external bushing or as integrated nut cooling.
External cooling: The ball screw nut is stuck into the cooling bushing. Ball screws can be cooled in this way without additional effort, even retrospectively.
Internal cooling: The cooling bushing is a fixed component of the ball screw nut. This cooling nut system is very compact and only requires minimum additional space.

Cooling of Spindle and Nut
The cooling of both components, spindle and nut, achieves the most optimal cooling effect.